
Industrial plant oil refining is a pivotal step to ensure the final product's quality, safety, and functionality. The refining stages—degumming, deacidification, decolorization, and deodorization—work synergistically to remove impurities and improve oil stability. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the degumming and deacidification stages, combined with process optimization techniques leveraging state-of-the-art continuous refining lines. It highlights operational parameters, impurity removal mechanisms, and advanced technologies that elevate oil color, smoke point, and oxidative stability.
Degumming primarily targets the removal of phospholipids, mucilaginous gums, trace metals, and other insolubles that adversely affect oil quality. In industrial settings, these hydratable and non-hydratable gums are separated by introducing water or acid solutions, facilitating their precipitation. Effective degumming reduces oil viscosity and latency, which enhances downstream processing efficiency and prevents deterioration.
| Impurity Type | Removal Method | Effect on Oil Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Phospholipids (Hydratable Gums) | Water washing / Acid degumming | Improves clarity, reduces turbidity |
| Non-hydratable Gums (Metal-complexed) | Acid degumming with citric acid or EDTA | Decreases oxidation catalysts |
| Trace Metals | Adsorption on activated clays | Reduces rancidity risk |
Free fatty acids (FFAs) significantly impact oil taste, stability, and shelf life. Industrial deacidification typically employs chemical alkali refining, where sodium hydroxide reacts with FFAs to form soaps subsequently removed by centrifugation. Alternatively, physical refining via steam distillation under vacuum offers advantages for oils with higher acidity.
Data from recent plant trials using a continuous refining line demonstrated that maintaining reaction temperatures within 70-85°C and vacuum levels near 5-10 mbar optimizes acid removal efficiency, reducing FFA content from ~3.2% to under 0.1%, which meets strict export food safety regulations.
“Optimizing vacuum and temperature parameters in continuous refining lines significantly cuts processing time and improves oil quality, a key factor for export-grade products.” – Dr. Lina M. Chuang, Food Process Engineer
Modern continuous refining equipment incorporates precision temperature control via PID loops, allowing incremental adjustments within ±1°C. Vacuum systems optimized with multi-stage pumps maintain stable negative pressure, critical for effective degassing and preventing oxidation.
Regarding adsorbent materials, trials comparing bleaching earth and activated carbon revealed that a tailored blend (approximate ratio 3:1) removes pigments and trace metals more efficiently, enhancing oil brightness from L* values of 45 up to 62 (measured by spectrophotometry) and improving oxidative stability by 30%.
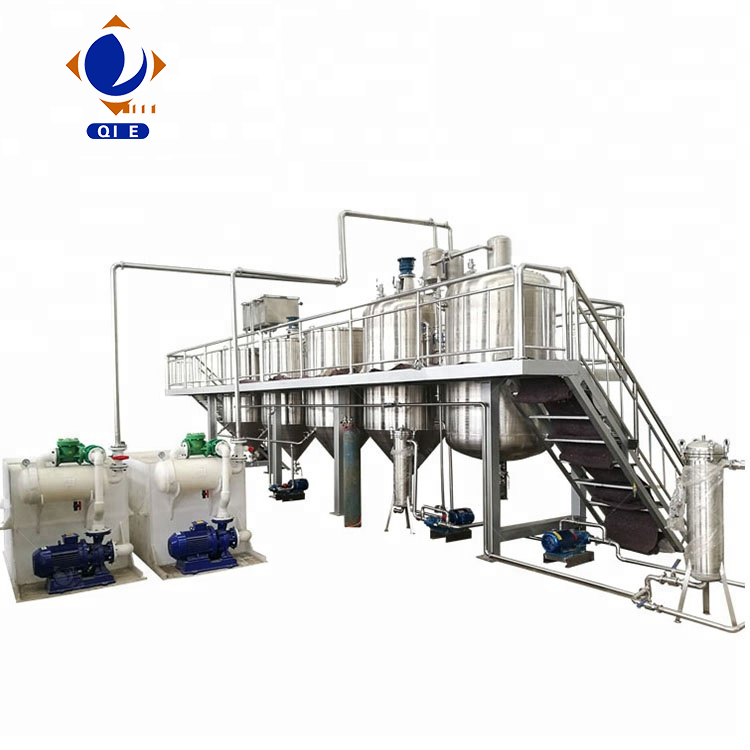

Consistency in oil quality hinges on diligent equipment maintenance. Recommended practices include:
For example, a leading customer utilizing Qi’e Group's internationally advanced continuous refining lines reported a 12% reduction in unplanned downtime and consistent product batches fully compliant with export-grade food safety certifications.
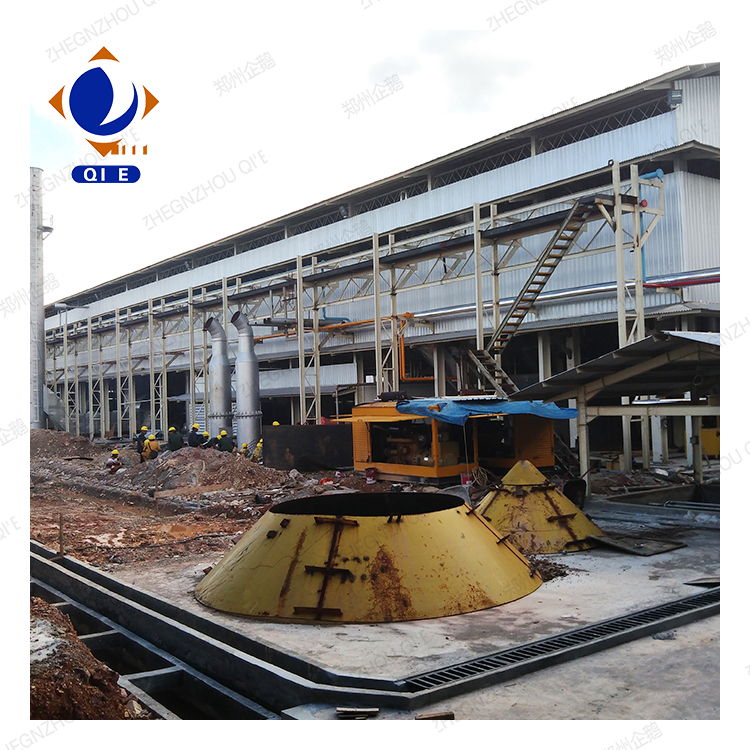

Real-world production data demonstrate remarkable improvements:
| Quality Indicator | Pre-Refining | Post-Refining | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Free Fatty Acid (FFA) % | 3.2% | 0.08% | 97.5% reduction |
| Color (Lovibond Units) | 22 Red / 12 Yellow | 5 Red / 3 Yellow | ~75% improvement |
| Smoke Point (°C) | 180°C | 230°C | 28% increase |
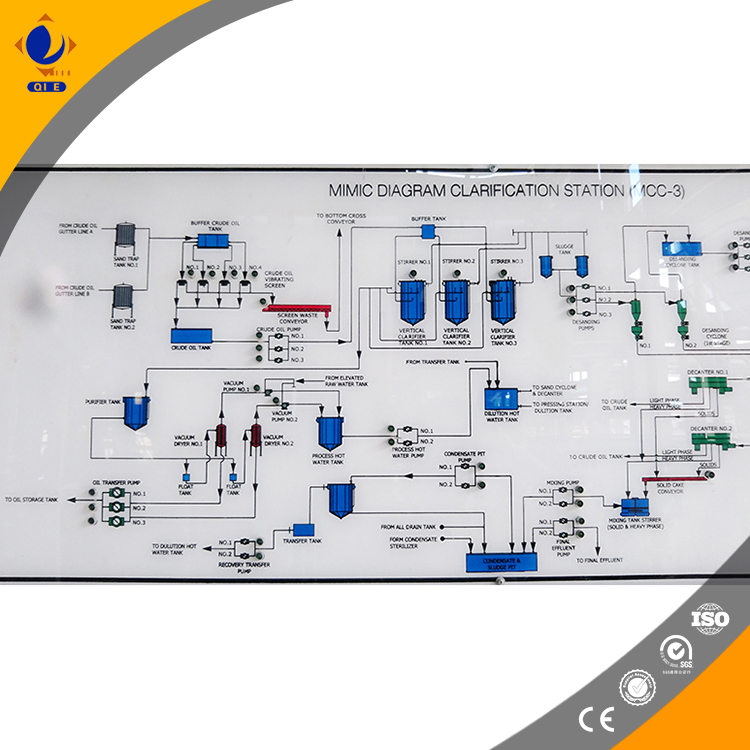
Leveraging these advancements, Qi’e Group implements globally certified continuous refining lines that guarantee every batch meets stringent export-grade food safety standards while maximizing operational efficiency.



