
In the realm of edible oil refining, degumming stands as the cornerstone, a critical first - step process that significantly influences subsequent refining stages and the overall stability of production equipment. This article delves deep into the physical and chemical mechanisms of degumming, offering insights for production managers to enhance efficiency and achieve consistent export - grade edible oil quality.
Degumming is not just a preliminary step; it is the linchpin that affects the effectiveness of neutralization, bleaching, and deodorization processes. By removing phospholipids, proteins, and other hydrophilic impurities, degumming ensures smoother operations in the subsequent refining steps and protects the equipment from potential damage caused by these impurities. For instance, if not properly removed, phospholipids can cause fouling in heat exchangers and reactors, reducing their efficiency by up to 30% according to industry reports. 
There are two main degumming techniques: hydration degumming and acid degumming. Hydration degumming is suitable for oils with relatively low phospholipid content, typically less than 2%. It involves adding water to the crude oil, causing the phospholipids to hydrate and separate from the oil phase. On the other hand, acid degumming is more effective for oils with higher phospholipid content or non - hydratable phospholipids. By adding acids such as phosphoric acid or citric acid, the non - hydratable phospholipids are converted into hydratable forms, facilitating their removal.
According to a study in the Journal of Food Science and Technology, acid degumming can achieve a phospholipid removal rate of up to 95% in some high - phospholipid oils.
The efficiency of impurity removal in degumming is highly dependent on several key process parameters, including temperature, pH value, and stirring speed. For example, a temperature range of 60 - 80°C is generally optimal for hydration degumming, as it promotes the proper hydration of phospholipids. The pH value also plays a crucial role; a slightly acidic pH (around 4 - 5) can enhance the separation of impurities. Stirring speed affects the contact between the oil and the degumming agent, with an appropriate speed ensuring uniform mixing and efficient impurity removal. 
In real - world production, issues such as cloudy oil or abnormal stratification may occur. These problems can be attributed to improper process parameters, insufficient degumming agent addition, or the presence of other contaminants. A systematic approach to troubleshooting involves checking the process parameters, analyzing the quality of the crude oil, and adjusting the degumming process accordingly. For example, if the oil is cloudy, it may be due to incomplete phospholipid removal, and increasing the degumming agent dosage or adjusting the temperature may solve the problem.
Different raw material oils, such as soybean oil and rapeseed oil, have different characteristics and require tailored degumming processes. Soybean oil usually has a relatively high phospholipid content, so acid degumming may be more appropriate. Rapeseed oil, on the other hand, may have specific impurities that need to be addressed during degumming. Understanding these differences can help production managers optimize the degumming process for each type of oil.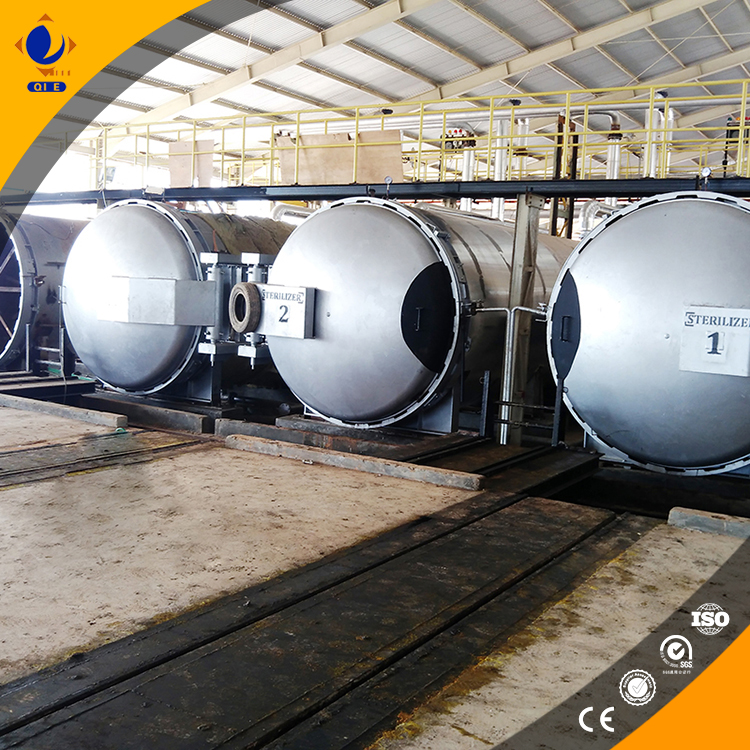 
Penguin Group's refining equipment supports the efficient implementation of degumming processes, ensuring that every drop of your oil meets international quality standards. With our advanced technology and reliable equipment, you can enhance the quality of your edible oil and gain a competitive edge in the global market. Explore how Penguin Group can help you achieve excellence in edible oil refining!



