
Industrial vegetable oil refining is a complex process that involves multiple steps to ensure the quality and stability of the final product. This guide focuses on the four core process units: degumming, deacidification, decolorization, and deodorization, and provides in - depth insights into the impurity removal techniques and process parameter optimization.
Degumming is the first step in vegetable oil refining, aiming to remove phospholipids, mucilage, and other impurities. Phospholipids can cause problems such as foaming and darkening during subsequent processing. The removal mechanism is based on the reaction of phospholipids with water or acid. For example, hydratable phospholipids can be removed by adding water, while non - hydratable phospholipids require the addition of acid. In modern continuous refining lines, precise temperature control, usually around 60 - 80°C, is crucial for efficient degumming. [Insert Image: 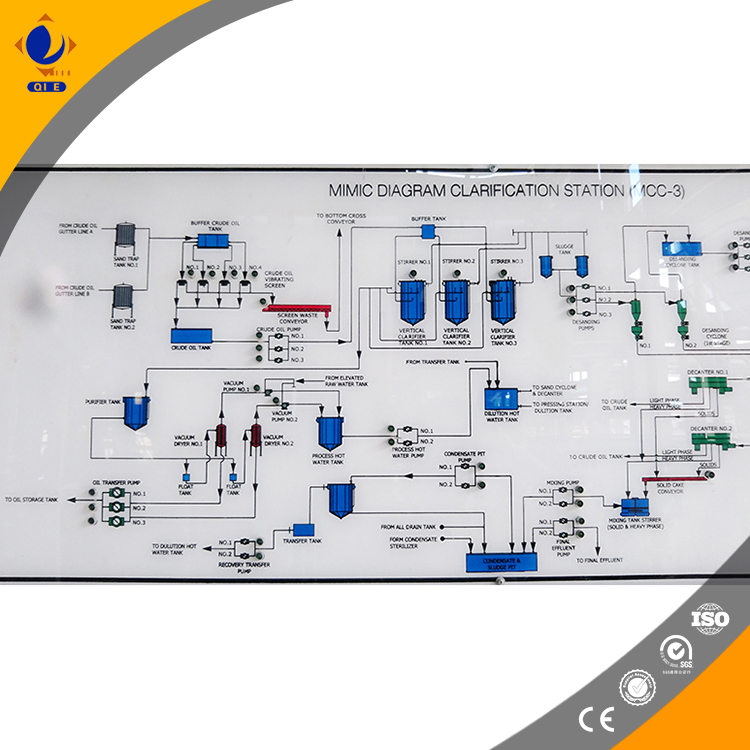 ]
]
Free fatty acids (FFAs) in vegetable oil can lead to unpleasant odors and reduced shelf life. Deacidification is used to remove these FFAs. The most common method is alkali refining, where an alkali solution is added to react with FFAs to form soapstock. The key parameters in this process are the amount of alkali added and the reaction temperature. A typical reaction temperature ranges from 70 - 90°C. By controlling these parameters, the FFA content can be reduced to less than 0.1%, significantly improving the quality of the oil.
Decolorization is mainly used to remove pigments such as carotenoids and chlorophyll from vegetable oil. Adsorption materials like activated clay or activated carbon are commonly used. The choice of adsorption material and the amount used are critical. In a modern continuous refining line, the temperature is usually maintained at 90 - 110°C under a vacuum environment to enhance the adsorption efficiency. After decolorization, the oil's color can be significantly improved, which is important for meeting market requirements. [Insert Image:  ]
]
Deodorization is the final step in vegetable oil refining, which aims to remove volatile compounds and improve the oil's oxidation stability. High - temperature steam distillation is commonly used in this process. The temperature is typically around 200 - 260°C under a high - vacuum environment. This process can effectively remove odorous compounds and reduce the peroxide value of the oil, thereby extending its shelf life.
Regular equipment maintenance is essential for the efficient operation of the vegetable oil refining process. For example, the filter cloth should be replaced every 2 - 3 months depending on the production volume. Regularly checking the equipment's sealing performance can prevent air leakage and ensure the stability of the vacuum environment. By optimizing the operation process and equipment maintenance, the production efficiency can be increased by 10 - 15%, and the product quality can be more stable. [Insert Image: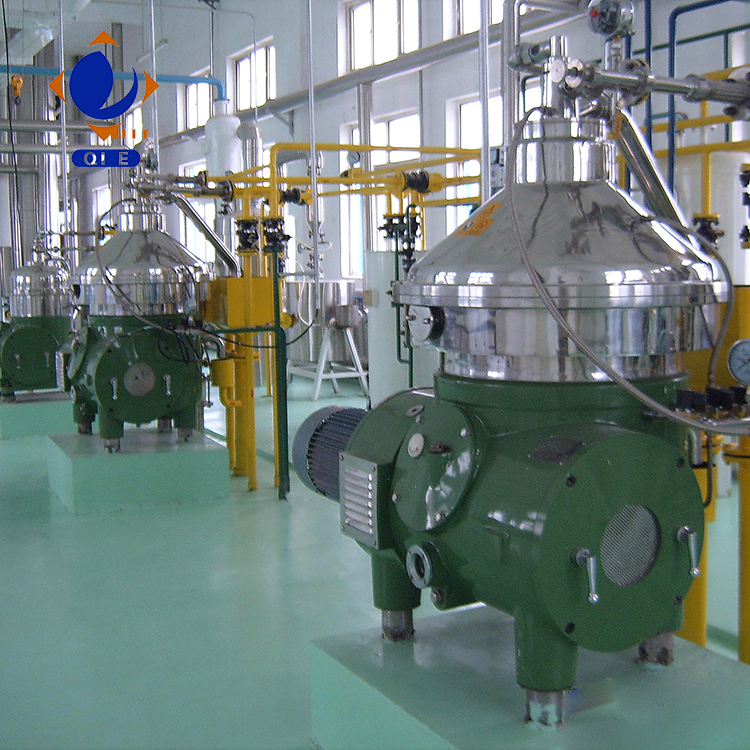  ]
]
含营销话术:Our advanced vegetable oil refining technology and comprehensive process optimization solutions can help you achieve higher product quality, meet export standards, and ensure long - term sustainable development. Don't miss this opportunity to enhance your production efficiency and competitiveness!
Ready to revolutionize your vegetable oil refining process? Click here to learn more about our cutting - edge technology and solutions.



