
Industrial-grade vegetable oil refining is a crucial process that plays a significant role in meeting international food safety standards. As the global demand for high-quality vegetable oils continues to rise, understanding the refining process becomes essential for export-oriented enterprises. This article delves deep into the four core processes of industrial-grade vegetable oil refining: degumming, deacidification, decolorization, and deodorization, and explores how modern continuous refining lines enhance oil quality.
In the international market, vegetable oil must meet strict food safety standards. Refining is the key step to remove impurities, improve oil quality, and ensure compliance with these standards. For example, refined vegetable oil has better color, higher smoke point, and longer shelf life, which are all important factors in determining its market value.
Degumming is the first step in the refining process, aiming to remove phosphatides and other gums from the crude oil. These impurities can cause the oil to become cloudy and affect its stability. By adding water or acid, the phosphatides are hydrated and separated from the oil. The efficiency of degumming can significantly impact the subsequent refining steps.
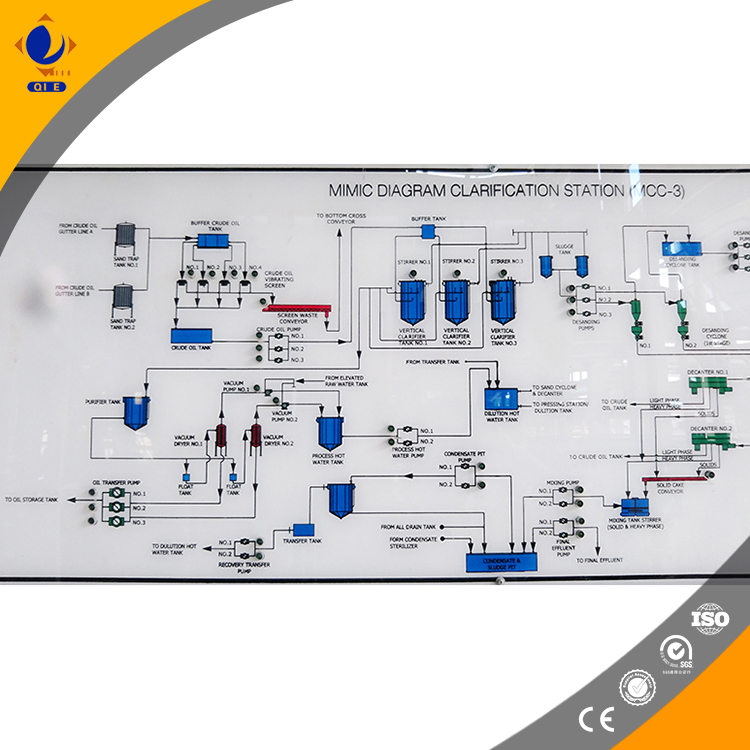
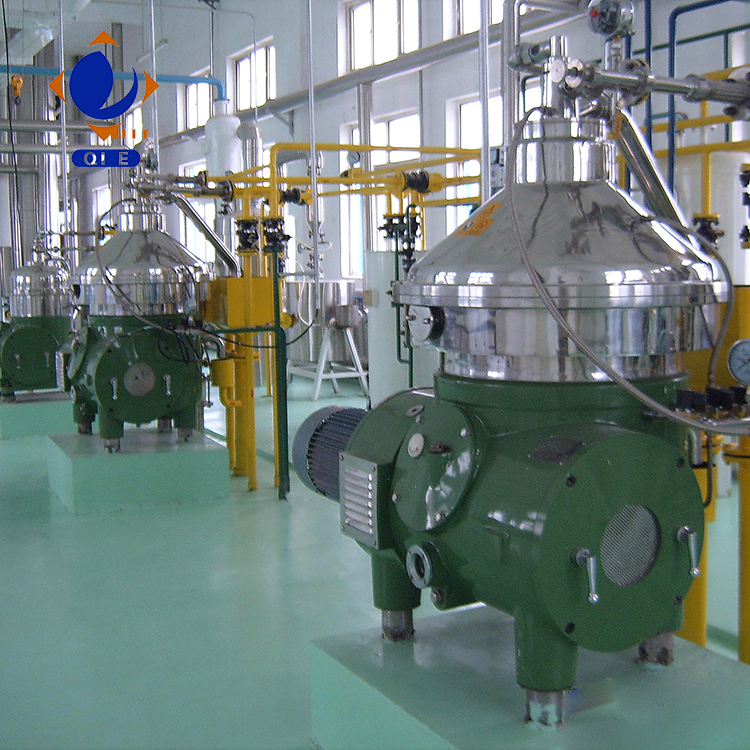
Free fatty acids in crude oil can lead to unpleasant odors and flavors. Deacidification is used to reduce the acid value of the oil. This can be achieved through physical or chemical methods. Physical deacidification, such as steam distillation under vacuum, is more environmentally friendly and can preserve the natural nutrients in the oil. Chemical deacidification involves the use of alkalis to neutralize the free fatty acids.
Decolorization is mainly to remove pigments, such as carotenoids and chlorophyll, from the oil. Adsorbent materials, such as activated clay and activated carbon, are commonly used. These materials can adsorb the pigments and improve the color of the oil. The choice of adsorbent and the operating conditions can affect the decolorization efficiency and the quality of the final product.

Deodorization is the final step to remove volatile compounds, such as odorous substances and some low-boiling-point impurities, from the oil. This is usually done under high temperature and vacuum conditions. The deodorization process can improve the flavor and oxidative stability of the oil.
Modern continuous refining lines are equipped with advanced technologies, such as precise temperature control, vacuum environment control, and optimized selection of adsorbent materials. These technologies can improve the refining efficiency and the quality of the final product. For example, by controlling the temperature and vacuum level accurately, the removal of impurities can be more effective, and the loss of nutrients in the oil can be minimized.
Actual production data shows that different process combinations can have a significant impact on the key indicators of oil quality, such as color, smoke point, and oxidative stability. For instance, a well-designed combination of degumming, deacidification, decolorization, and deodorization can increase the smoke point of the oil by up to 20%, and improve the oxidative stability by 30%. This not only enhances the market competitiveness of the oil but also meets the requirements of high-end customers.
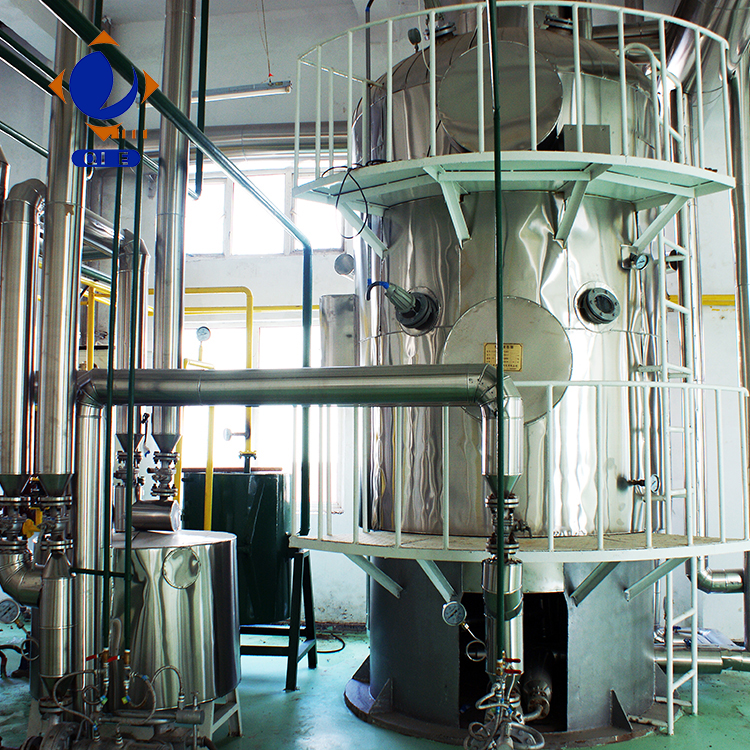

In addition to understanding the refining process, proper maintenance of the refining equipment is also crucial for ensuring the quality and efficiency of production. Here are some practical maintenance tips for operators:
Qi'e Group, for example, adopts an internationally leading continuous refining system. This system ensures that each batch of oil meets the standards of the European Union and the FDA. Through years of practice, Qi'e Group has accumulated rich experience in vegetable oil refining and has provided high-quality products to customers around the world.
If you are looking for reliable vegetable oil refining solutions and want to improve your product quality, click here to learn more.



