
In the industrial - grade vegetable oil refining process, removing impurities is a crucial step. This article comprehensively covers the entire refining process, with a focus on four core process units: degumming, deacidification, decolorization, and deodorization.
Degumming is the first step to remove phospholipids and other gummy substances from crude vegetable oil. Phospholipids can cause oil to become cloudy and affect its stability. For example, in a large - scale vegetable oil refinery, by using water - degumming method, the phospholipid content can be reduced from about 500 ppm to less than 100 ppm. The key is to control the temperature at around 60 - 70°C and the water addition amount at about 2 - 3% of the oil volume.

Deacidification is mainly to remove free fatty acids in the oil. Alkaline refining is a common method. By adding an appropriate amount of sodium hydroxide solution, free fatty acids react with alkalis to form soapstock, which can be separated from the oil. In practice, the acid value of the oil can be reduced from 3 - 5 mg KOH/g to less than 0.1 mg KOH/g through this process, significantly improving the quality of the oil.
Decolorization aims to improve the color of the oil by using adsorbents such as activated clay and activated carbon. These adsorbents can adsorb pigments, peroxides, and other impurities in the oil. In a continuous decolorization process, with the right selection of adsorbents and proper control of temperature (about 90 - 110°C) and time (about 20 - 30 minutes), the Lovibond color value of the oil can be reduced by 50 - 70%.

Deodorization is the last and also a very important step. It removes volatile substances, odors, and some remaining impurities in the oil. By using high - temperature and high - vacuum conditions (temperature around 200 - 250°C and vacuum degree below 2 mbar), the oil's smoke point can be increased from about 180°C to over 230°C, and the oxidation stability can be significantly improved.
Modern continuous refining lines play a key role in the vegetable oil refining process. Precise temperature control, vacuum environment control, and the selection of adsorption materials are crucial for purification effects. For example, in a continuous refining line, accurate temperature control within ± 2°C can ensure the stability of the reaction process. The right vacuum environment can effectively remove volatile substances, and the selection of high - quality adsorption materials can improve the adsorption efficiency.
Through actual production data, we can see that different process combinations have significant impacts on the product's color, smoke point, and oxidation stability. For instance, a process combination of degumming - deacidification - decolorization - deodorization can improve the oil's oxidation stability by about 30 - 50%, and increase the smoke point by 20 - 30°C compared with unrefined oil.
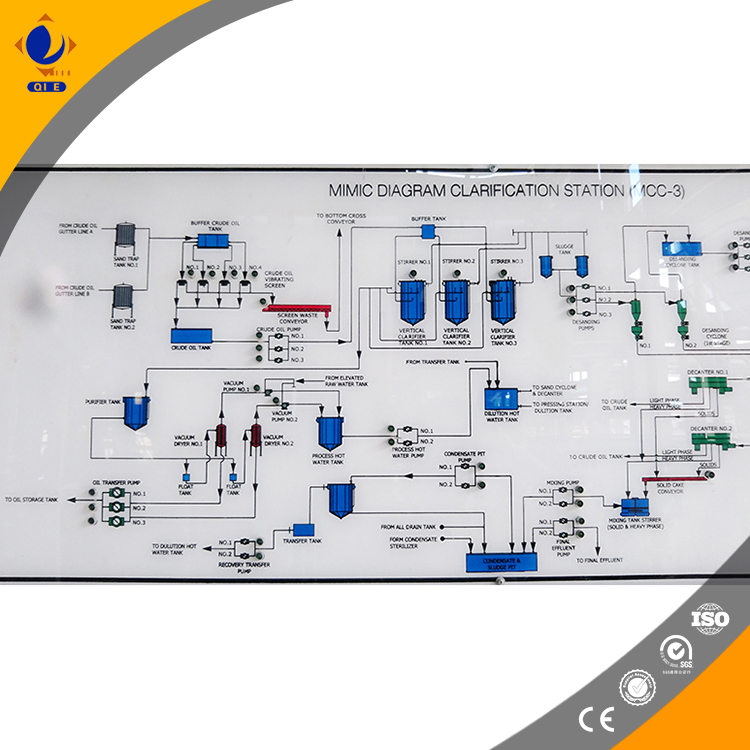
In addition to process technology, equipment maintenance is also very important. For example, the filter cloth replacement cycle should be about every 10 - 15 days in continuous operation to ensure the filtering effect. Regular equipment seal detection can prevent air leakage, which is crucial for maintaining a stable vacuum environment.
In conclusion, by understanding and mastering these key techniques in vegetable oil refining, enterprises can achieve high - efficiency and sustainable production. Choose Qi'e Group's advanced oil solvent extraction and continuous refining technology to help produce high - quality vegetable oils and ensure your products stand out in the market competition. Click here to learn more about our technology solutions.



